position
The position property defines the positioning method of an element. The position is adjusted by defining the values for top, bottom, left and right.
Syntax
position: static | relative | fixed | absolute | sticky;Example
.container{
border: 1px solid black;
}
.div-1 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: red;
}
.div-3 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.div-2 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: yellow;
position: static;
}
.div-2 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: yellow;
position: relative;
top: 5px;
left: 5px;
}
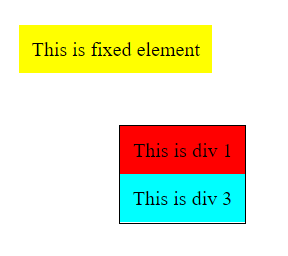
.div-2 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: yellow;
position: fixed;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
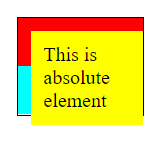
container{
border: 1px solid black;
position: relative;
}
.div-2 {
padding: 10px;
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
Property Values
static: The elements are positioned according to the normal flow of the page. (Default value)
relative: The element is positioned relative to its original position.
fixed: The element is positioned relative to the window. So. the element always remains at the specified position even when the page is scrolled.
absolute: The element is positioned relative to its nearest positioned ancestor. If the element has no positioned ancestors then it uses the document body and moves along with page scrolling.
sticky: The element is positioned relative to the user's scroll position. It is positioned relative until it reaches the given position in the viewport then it sticks in the given position like position:fixed.