Let’s learn how to perform pagination in elastic search with Node.js. But before that, let us look at a brief description of elastic search.
Elastic search is a search engine based on the Lucene library. It provides a full-text search engine with an HTTP interface. The data is stored in the form of the schema-free JSON format. Elastic search is popular for full-text search. It provides scalable search, with a near real-time search capability. The communication with the elastic search happens through HTTP-based REST.
Requirements:
Create a node application
Initialize a node application
$ mkdir es-node && cd es-node
$ npm init -y
Install required packages and create an index file
$ npm install express dotenv axios
$ touch index.js
$ code .
$ touch .env
Create express server
Let’s create an express server, and add all the required dependencies
ESENDPOINT= YOUR-ELASTIC-SEARCH-ENDPOINT
PORT= 5000const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const axios = require("axios");
require("dotenv").config();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
const ESENDPOINT = process.env.ESENDPOINT;
app.get("/", (req, res) => {});
app.listen(PORT, console.log(`Server started at PORT: ${PORT}...`));We will add all the code for searching in the HTTP GET http:localhost:5000/.
Code for achieving pagination in elastic search
For efficient pagination in elastic search we need to do the following things:
sort: Sorts the entire data according to the given key e.g.createdAtsearch_after: Searches after the sort data in this case thecreatedAtsize: The size of the received data
Structure of search query
elasticSearchQuery = {
size: 10,
query: {
bool: {
must: searchArray,
},
},
sort: sort: [{ createdAt: { order: "desc" } }], //* sorts data in descending order,
search_after: ["2022-05-31T05:11:10.667Z"], //* createdAt data
}In the above code, the size determines the size of the searched and return data. Sort determines the key to be sorted and the type of sort, them being asc for ascending and desc for descending. Now the key search_after takes in the value of createdAt because, the sorting is done through that key. It sorts the data and finds the exact createdAt time and gives the set of data right after the object containing the createdAt value.
Implementation
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const axios = require("axios");
require("dotenv").config();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
const ESENDPOINT = process.env.ESENDPOINT;
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
try {
//* size of data
const limit = parseInt(req.query.limit) || 100;
//* search after key
let lastEvaluatedKey = req.query.lastEvaluatedKey;
const searchArray = [
{
match: {
status: {
query: "approved", // product with the value of approved are only searched for
},
},
},
];
let finalESQuery = {
size: limit,
query: {
bool: {
must: searchArray,
},
},
sort: [{ createdAt: { order: "desc" } }],
};
//* for first
if (req.query.lastEvaluatedKey) {
finalESQuery["search_after"] = [lastEvaluatedKey];
}
const apiResponse = await axios({
method: "get",
url: `${ESENDPOINT}/products/_search?filter_path=took,hits.hits._source`,
data: finalESQuery,
});
//* Pagination (start): check if next set of data exists in ES
//* value of createdAt of last data recieved data
lastEvaluatedKey =
apiResponse.data.hits.hits[apiResponse.data.hits.hits.length - 1]._source
.createdAt;
let hasNext = false;
let nextVal = {
size: limit,
query: {
bool: {
must: searchArray,
},
},
search_after: [lastEvaluatedKey],
sort: [{ createdAt: { order: "desc" } }],
};
//* searching if next set of data exists and if it exists making hasNext true
const nextResponse = await axios({
method: "get",
url: `${ESENDPOINT}/products/_search?filter_path=took,hits.hits._source`,
data: nextVal,
});
if (nextResponse.data.hits) {
hasNext = true; //* If next set of data is found makes hasNext true
}
//* Pagination (end)
const data = {
data: apiResponse.data.hits.hits,
pagination: {
lastEvaluatedKey: lastEvaluatedKey,
hasNext: hasNext,
},
};
res.json(data);
} catch (error) {
res.json(error);
}
});
app.listen(PORT, console.log(`Server started at PORT: ${PORT}...`));
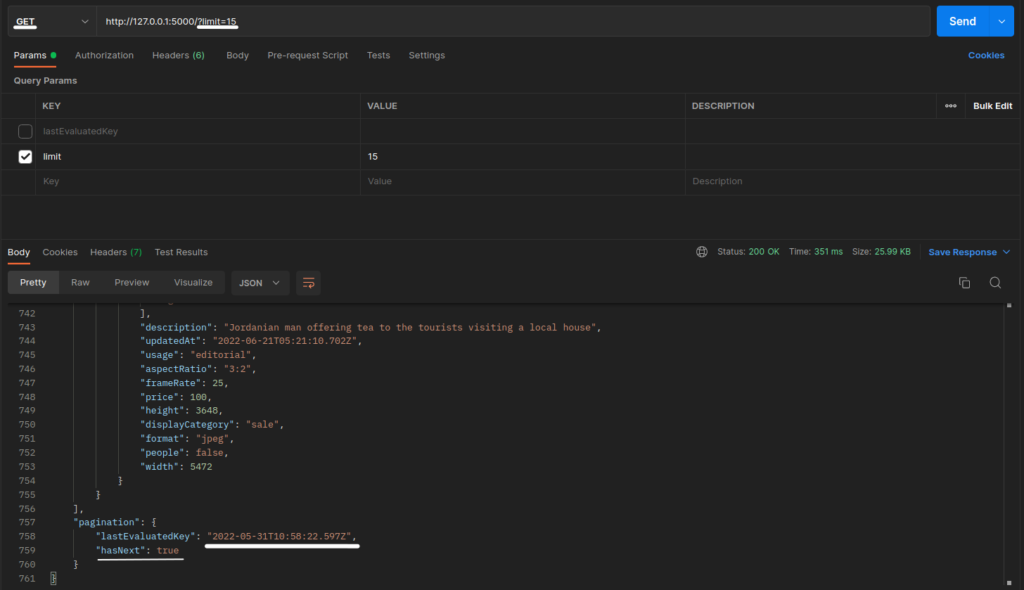
Now let’s test the code out from the postman by sending an HTTP GET request at http://localhost:5000.
Output
Let’s again hit the API, now will add the received lastEvaluatedKey and get the second page of data.
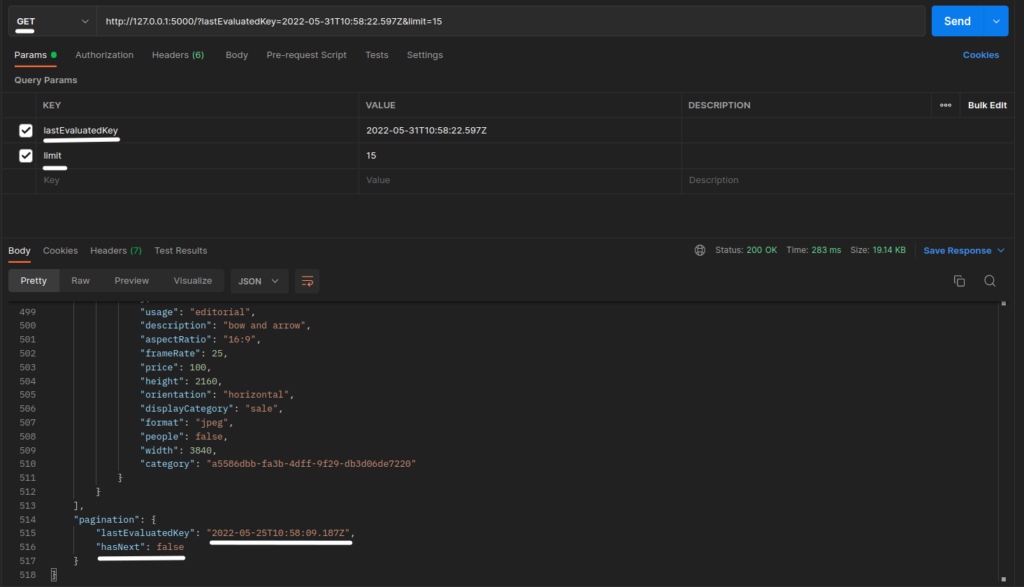
We can see from the response that there is no page after the second page because the hasNext key has the value of false, telling us that there is no 3 page to be fetched. So, this is how we perform pagination in elastic search through nodejs.
Conclusion
In this article saw and learned how to use search_after key to perform pagination in elastic search with nodejs. If you want to learn about paginating other technologies Pagination In DynamoDB Using Node JS can be a great starting point.
