Introduction to JavaScript
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted/ just-in-time programming language that is one of the few core technologies of the World Wide Web, along side with HTML and CSS. JavaScript is a popular programming language and scripting language as according to the stats, over 97% of websites use JavaScript. All major browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine . JavaScript is very easy to implement because it is integrated with HTML. It is open and cross-platform. JavaScript works on both front end and back end side of a application
A Brief History
- It was introduced to the outside world in September 1995 by Netscape Communications Corporation and created by a programmer named Brendan Eich. It took Eich only 10 days to create the scripting language, which was first known as Mocha. JavaScript was firstly known as a ‘UI glue’, and was used by designers.
- In 1997, ECMAScript was born making the programming language properly maintained and managed. ECMAScript languanges include JavaScript and ActionScript.
- One of the major feature came to JavaScript in 2005, it was Ajax. Making websites dynamic instead of static.
- In, 2009 Ryan Dahl introduced first server-side JavaScript environment, Node.js. Which made it possible for JavaScript to run as a server side language.
Writing First JavaScript Code
A brief note before writing JavaScript code is that JavaScript code goes inside the <script>...JavaScript Code Lies Here...</script> tag.
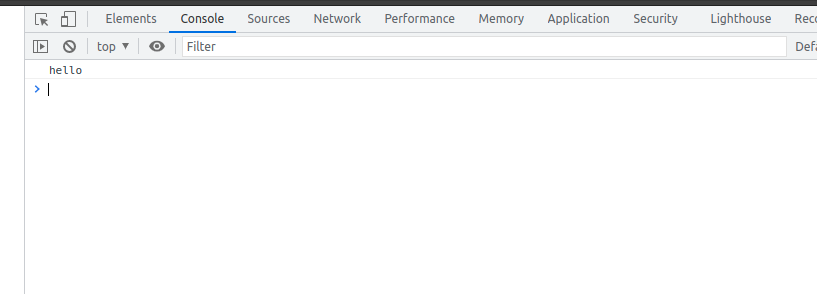
Writing to the console
<html>
<head>
<title>First JavaScript program writing to the console</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log("hello");
</script>
</body>
</html>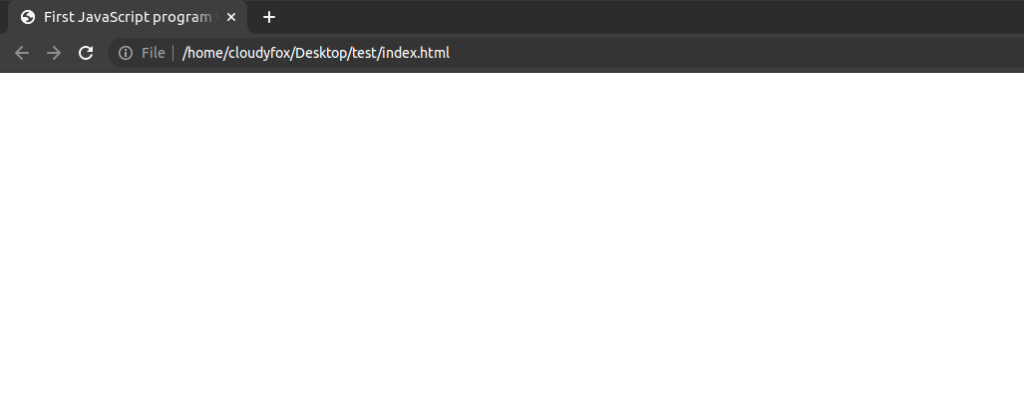
Setting up an alert
<html>
<head>
<title>First JavaScript program writing to the console</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
alert("hello");
</script>
</body>
</html>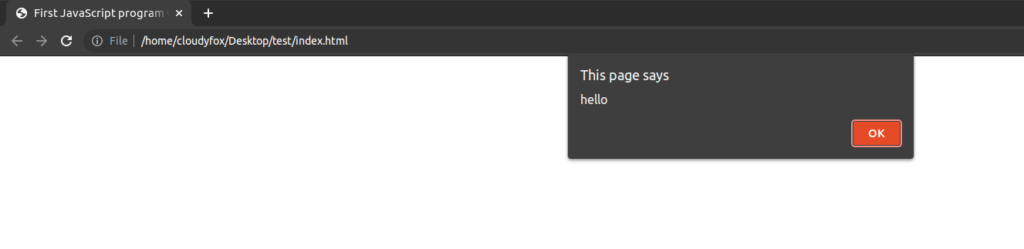
Operators and Data types in JavaScript
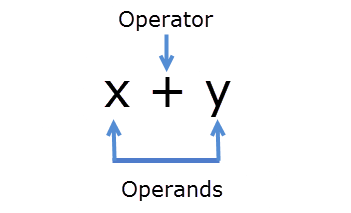
What is an Operator?
In computer science, an operator is a character or characters that determine the action that is to be performed to operands.
Operators Present in JavaScript
Arithmetic Operators
let x = 10;
let y = 20;
console.log("x + y = ", x + y);
console.log("x - y = ", x - y);
console.log("x * y = ", x * y);
console.log("x / y = ", x / y);
console.log("x % y = ", x % y); // remainder
console.log("x ** y = ", x ** y); // exponential
console.log("++ y = ", ++ y); // pre
console.log("-- y = ", -- y);
console.log("y ++ = ", y ++); // post
console.log("y -- = ", y --);Assignment Operators
Comparison Operators
Logical Operators
Type Operators
What are Data types?
In computer science and computer programming, a data type or simply type is an attribute of data which tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data.
Data Types Present in JavaScript
String
let name = " scanskill ";
name = ' Scan Skill ';
name = ` This is ScanSkill `;Number
let number = 10; // integers
number = 409.05; // floating points
number = 1.55e+6; // exponential -> 1550000BigInt
let bigInt = 1908808n;
bigInt = 1n;Boolean
let isRunning = false;
isRunning = true;Object
let object = { };
object = { name: "Scan Skill", rollNumber: "1" };
object = { "name": "Scan Skill", "rollNumber": "1" };Array
let array = [];
array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ];
array = [ "a", "b", "c" ];
array = [ { name: "scan skill" },{ name: "cloudy fox" } ];Function
let name = function () {
console.log("Hello from name function");
}
name = () => {
console.log("another way to create same function");
}Null
let value = null;Undefined
let value; // not defined so it returns undefinedConditional Statements
IF ELSE statements
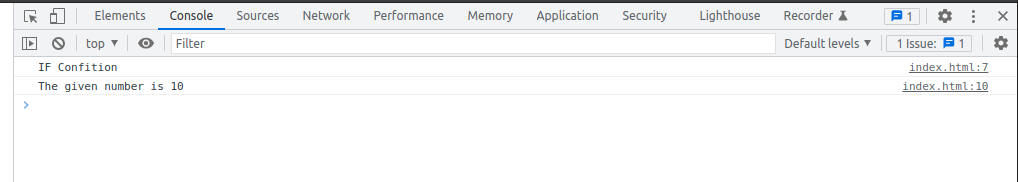
IF Condition
const number = 10;
if(number === 10) {
console.log("The given number is 10");
}
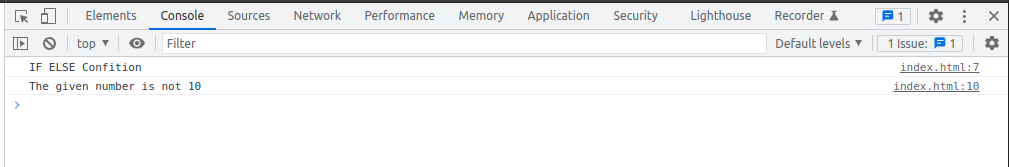
ELSE Condition
const number = 20;
if(number === 10) {
console.log("The given number is 10");
}
else {
console.log("The given number is not 10");
}
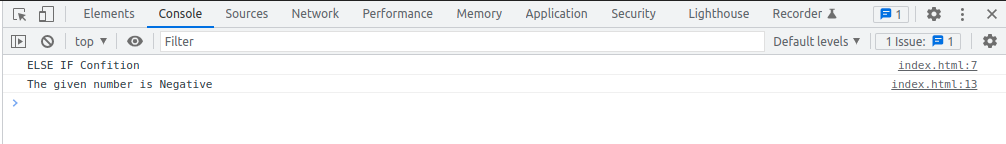
ELSE IF condition
console.log("ELSE IF Confition")
const number = -2;
if(number > 0) {
console.log("The given number is Positive");
}
else if(number < 0) {
console.log("The given number is Negative")
}
else {
console.log("The given number is Zero");
}
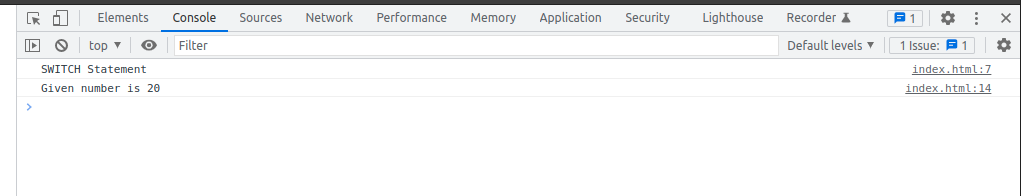
Switch statements
const number = 20;
switch (number) {
case 10:
console.log("The given number is 10")
break;
case 20:
console.log("Given number is 20");
break;
default:
console.log("Default condition");
break;
}
Looping Statements
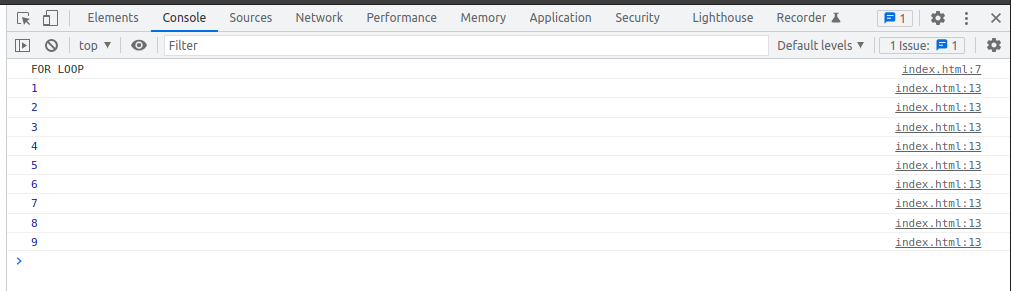
FOR Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
for(let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
console.log(array[i]);
}
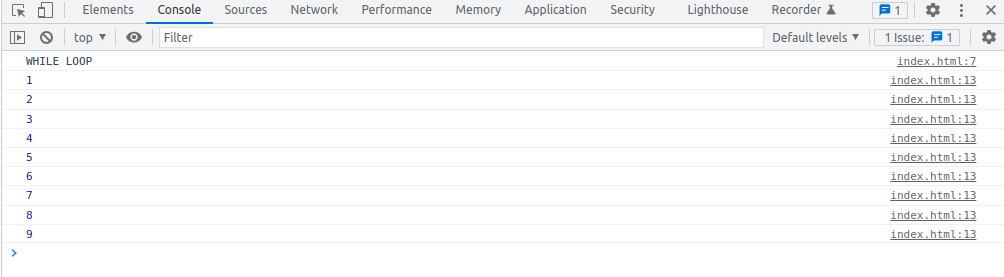
WHILE Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
let iterator = 0;
while (iterator < 9) {
console.log(array[iterator]);
iterator ++;
}
DO WHILE Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
let iterator = 0;
do {
console.log(array[iterator]);
iterator ++;
}while (iterator < 9)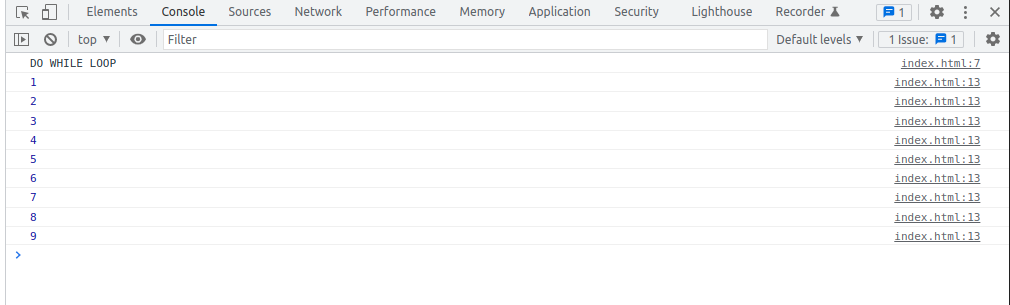
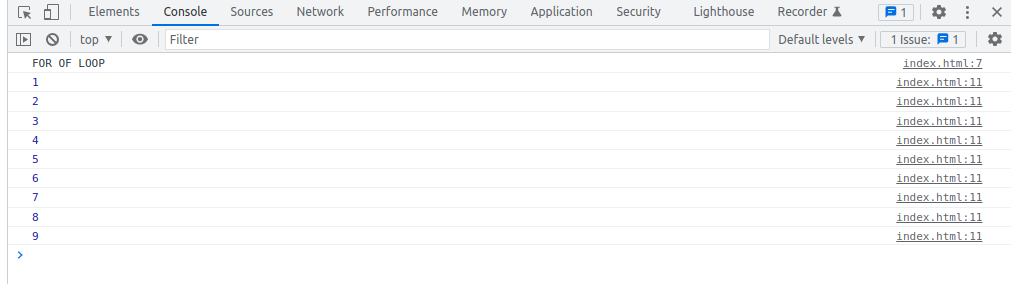
FOR OF Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
for(let number of array) {
console.log(number);
}
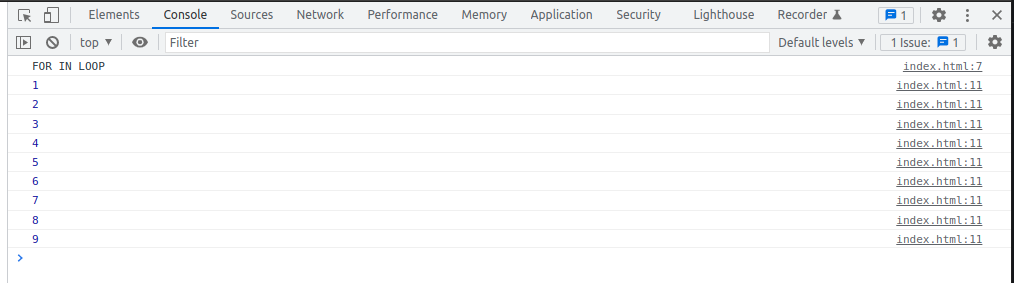
FOR IN Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
for(let number in array) {
console.log(array[number]);
}
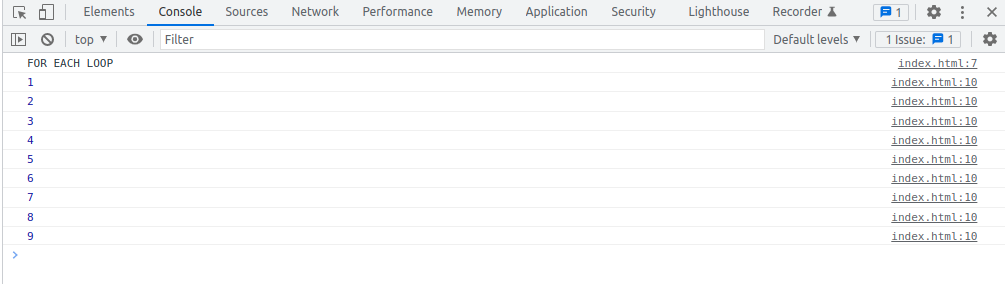
FOR EACH Loop
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
array.forEach(( number ) => console.log(number));
// OR
array.forEach(function(number) {
console.log(number);
})
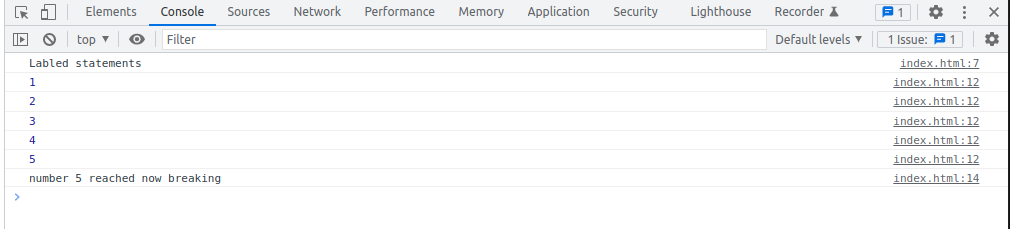
Labeled Statements
const array = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ];
breakPoint:
for(let number of array) {
console.log(number);
if(number === 5) {
console.log("number 5 reached now breaking");
break breakPoint;
}
}
Class, Object, And Function
Class in JavaScript
Classes are a template for creating objects. To declare a class, you use the class keyword with the name of the class
class User {
constructor (name, roll){
this.name = name;
this.roll = roll;
}
getUserDetail() {
console.log("The name is ", this.name, " and the roll number is ", this.roll)
}
}
const user = new User("Scan Skill", 40);
user.getUserDetail();
Object in JavaScript
In JavaScript, an object is a standalone entity, with properties and type. There are two ways of initializing or defining objects in JavaScript, first one is through class and another is wrapping key value pairs inside curly braces { } .
Normal Objects
const userObject = {
name: "Scan Skill",
roll: 40
}
console.log(typeof userObject);
Object made from class
class User {
constructor (name, roll){
this.name = name;
this.roll = roll;
}
getUserDetail() {
console.log("The name is ", this.name, " and the roll number is ", this.roll)
}
}
const user = new User("Scan Skill", 40);
console.log(typeof user)
Function
A function is a reusable block of code made to perform set specific operations.
//*
function name () {
console.log("This is the first way of creating a function");
}
let nameOne = function () {
console.log("This is the second way of creating a function");
}
const nameTwo = () => {
console.log("This is the third way of creating a function");
}
Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve saw a overview on JavaScript, and how it works with examples.